- uses a "cabling" system that guides the data signals along a specific path.
- the data signals are bound by the "cabling"system.
- also known as Bound Media.
- the message flows through a physical media such as twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable, or fiberoptic cable.
- Twisted Pair
- Coaxial Cable
- Optical Fiber
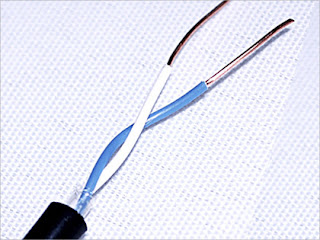
Twisted Pair Cables consist of two conductors, each with its own plastic insulation. There are Two types of Twisted Pair Cable, the Shielded and Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable. The Shielded Twisted Pair is a Pair is a type of cable originally developed by IBM for token Ring that consist of two individual wires wrapped in a foil shielding to help provide a more reliable data communication. Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable on the other hand is a popular type of cable used in computer networking that consist of two shielded wires twisted around each other. These Cables are twisted to minimize the electromagnetic interference. The UTP and STP are braided to prevent noise or crosstalk. Its socket is RJ45. The common applications of Twisted Pair are telephone lines to provide voice and data channels, DSL lines to provide high data rate connections, LANs as 10BaseT.
Coaxial Cable

Coaxial Cable offers longer distances and better speeds compared to twisted Pair, due to shielding. The inner conductor is held inside an insulator with the other conductor woven around it providing a shield.
Types of Coaxial Cable
- Hard Line - are the powerful cables with rigid outer shield and with minimum loss. Normally used to connect a transmitter and an antenna. These cables consist of high dielectric in high temperature as well.
- Tri axial - cable with three layers of shielding and the outermost shielding protecting the inner layers from outer electromagnetic interference.
- Twin axial - This cable consist of twisted pair covered by shield.
- Bi axial - consist of two 50O coaxial cables used for networking.
- Semi rigid - it is a coaxial cable with solid outer copper sheath.
Optical Fiber

It is similar to the copper wire system that fiber-optics is. Its difference is that fiber optics use light pulses to transmit information down fiber lines instead of using electronic pulses to transmit information down copper lines
Types of Optical Fiber:
- Distribution Cables - are composed of several small, tightly buffered fibers reinforced with fiberglass rods. The design of these cables keeps them from tangling.
- Breakout Cables - Breakout cables are larger and sturdier than distribution cables, however, they are also more expensive. Instead of being bundled together, they are individually reinforced, which makes it easier to terminate their connections.
- Loose Tube Cables - contain several fibers bundled together in a small plastic tube. However, these cables are not strong as other types, so they have to be handled with care.
- Ribbon Cable - are fiber optic cables that contain approximately 12 fibers in a row, which keeps them from tangling. These cables are filled with gels that prevent moisture from collecting around the tubes.
- Aerial Cable - are the types of fiber optic cables generally installed on outside poles. They are constructed of strong, durable materials that can withstand weather conditions.
UNGUIDED MEDIA
- doesn't use any physical connectors between the devices communicating.
- usually the transmission is send through the atmosphere but sometime it can be just across the rule
- wireless medial is used when a physical obstruction or distance blocks are used with normal cable media.
- Radio Waves
- Micro Waves
- Infrared Waves
Simply are bunch of radio waves when you put them into group. The electromagnetic spectrum covers a wide range of wavelengths and photon energies. Light used to "see" an object must have a wavelength about the same size as or smaller than the object. The ALS generates light in the far ultraviolet and soft x-ray regions, which span the wavelengths suited to studying molecules and atoms.
Radio Waves

It has frequency between 10 khz to 1ghz. They're common in radio broadcast, amateur radio, television, and mobile phones. Radio waves have much longer wavelength that light waves. The electrons in a piece of copper wire move; this means that they generate electric currents in the wire.
Micro Waves

Unlike Radio Waves, Micro waves travels at high frequency and provide through put as a wireless network media. Micro waves transmission requires the sender to be inside of the receiver. Micro Waves have such a short wavelength that they are very easily absorbed by water, that's the reason why they are very easily absorbed by water, that's the reason why they are used in microwave ovens.
Infrared Waves
Infrared frequencies are just below visible light.These high frequencies allow high speed data transmission. This technology is similar to the use of a remote control for a TV. Infrared transmission can be affected by objects obstructing sender or receiver.
No comments:
Post a Comment